Understand React Components: A Comprehensive Guide
React components are the building blocks of React applications. They allow developers to create reusable and modular code, making it easier to manage complex UIs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of React components, including their types, lifecycle methods, props, state management, and more.
Understanding React Component Types
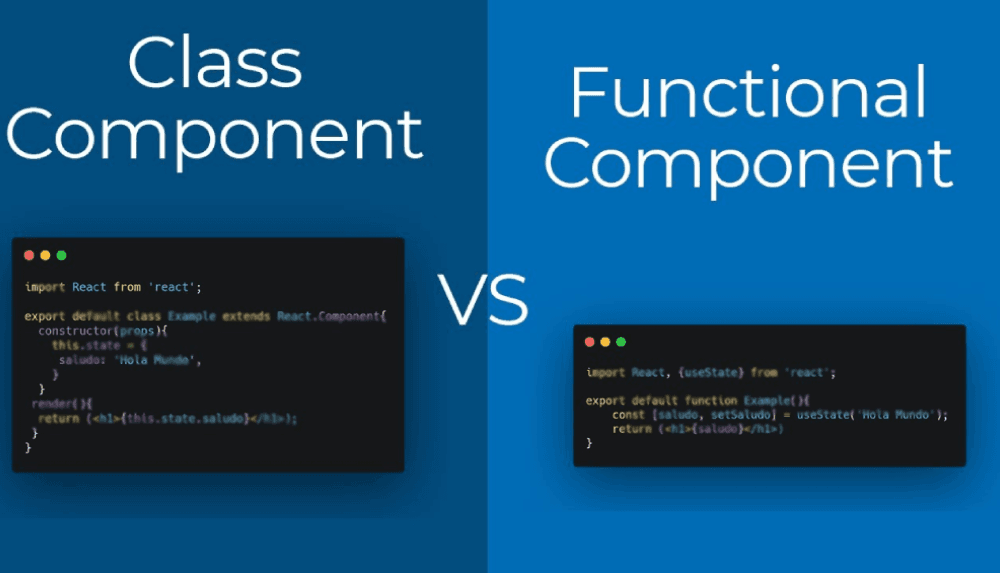
In React, there are two primary types of components: functional and class-based components.
Functional Components
Functional components are stateless components that do not have access to the component's context. They are often used for simple, reusable UI elements like buttons or headers.
// Simple functional component
function HelloWorld() {
return <div>Hello World!</div>;
}Class-Based Components
Class-based components are stateful components that inherit from React's
Component// Simple class-based component
class Counter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { count: 0 };
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {this.state.count}</p>
<button onClick={() => this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 })}>
Increment
</button>
</div>
);
}
}React Component Lifecycle Methods
React components have a lifecycle, which consists of several methods that are called at different stages of the component's life cycle. These methods provide opportunities for you to execute custom code during specific points in the component's life.
componentDidMount()
The
componentDidMount()import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
console.log('Component mounted');
}
render() {
return <div>Hello World!</div>;
}
}componentDidUpdate()
The
componentDidUpdate()import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('Component updated');
}
render() {
return <div>Hello World!</div>;
}
}Props and State Management
Props (short for "properties") are immutable values passed from a parent component to a child component. State is an object that stores data used by the component.
Props
Props are typically passed as attributes when creating a JSX element.
import React from 'react';
class Greeting extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>Hello, {this.props.name}!</div>;
}
}
// Using props in a parent component
const Parent = () => {
const name = 'John Doe';
return <Greeting name={name} />;
};State Management
State management involves updating the component's state to reflect changes in the UI.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
class Counter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { count: 0 };
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {this.state.count}</p>
<button onClick={() => this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 })}>
Increment
</button>
</div>
);
}
}Conclusion
In conclusion, React components are a powerful tool for building reusable and modular UIs. By understanding the different types of components, lifecycle methods, props, and state management, you can create robust and efficient React applications.
Actionable Advice:
Start by creating simple functional or class-based components to practice rendering JSX elements.
Experiment with using props and state management to update your component's UI.
Explore further resources to learn more about React components and their various use cases.

Kiran Chaulagain
kkchaulagain@gmail.com
Software engineer and DevOps practitioner with 6+ years of experience turning ideas into scalable web applications and reliable infrastructure. Passionate about clean code, automation, and bridging the gap between development and operations.